Understanding heart failure
What is heart failure?
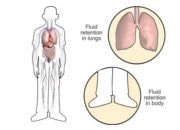
In heart failure, the heart muscle fails to deliver sufficient amounts of blood, nutrients and oxygen to the many organs of a human body. It is a serious medical condition often associated with fluid overload in the lungs, the legs, or other parts of the body. Therefore, heart failure is frequently also referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF).
What are the symptoms and consequences of heart failure?
Typical symptoms experienced by persons with heart failure are shortness of breath (also called dyspnea), fatigue, and exercise intolerance. In persons over 65 years of age, it is the most common cause of hospitalisation.
Why does heart failure develop?
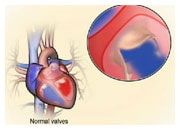
There are many conditions that lead to the development of heart failure. Frequent causes are coronary artery disease (i.e., narrowed blood vessels in the heart muscle), high blood pressure, rhythm or heart valve problems.
There are two principal problems that may lead to heart failure:
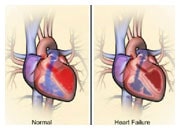
1) the heart muscle is too weak, which leads to pump failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF); or
2) the heart muscle has preserved function (HFpEF) but has become too stiff to work efficiently.
It is important to diagnose heart failure as early as possible, because for many underlying causes there is very effective treatment. Diagnosis can be enhanced using blood tests (e.g. natriuretic peptide), and always should include an echocardiogram, which is an ultrasound-based examination of the heart offered by a heart specialist (cardiologist).
Can heart failure be treated?
With the right treatment started in time, the grave signs and symptoms of heart failure can be controlled and frequently reversed. Since the options should be tailored to the specific needs of an individual, it is very important to collect information on possible choices as early as possible.
The range of remedies that can be applied in patients with heart failure is very wide. It almost always includes medical drugs (tablets) and changes in lifestyle and diet. Some patients benefit from the implantation of dedicated devices like a pacemaker or defibrillator, and some from surgery up to the possibility of a heart transplantation or the implantation of a ventricular assist device (VAD). Although heart failure is serious, most patients will benefit from treatment and can continue to lead active and enjoyable lives.