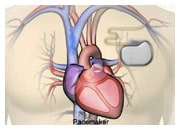
What is heart failure?
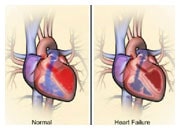
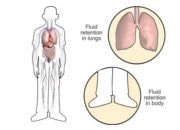
Heart failure is a serious medical condition where the heart does not pump blood around the body as well as it should. This means that your blood can’t deliver enough oxygen and nourishment to your body to allow it to work normally. This, for example, may cause you to feel tired or fatigued. It also means that you can’t eliminate waste products properly – leading to a buildup of fluid in your lungs and other parts of your body, such as your legs and abdomen.
Heart failure often develops because you have (or had) a medical condition affecting your heart, such as coronary artery disease, a heart attack or high blood pressure, which has damaged or put extra workload on your heart. These are the most common reasons why you may have developed heart failure. However, there are many other reasons why you may have heart failure, including heart blood pressure, coronary artery disease, valvular heart disease, heart muscle disease and arrhythmias.
Heart failure can develop at any age but clearly becomes more common with increasing age. Around 1% of people under 65 years of age have heart failure, but 7% of 75-84-year-olds have heart failure and this increases to 15% in people older than 85. It is the most common cause of hospitalisation in patients over 65 years of age.
Although it is called heart ‘failure’, this doesn’t mean that your heart is about to stop working. It does mean that your heart is having difficulty working to meet the needs of your body (especially during activity).